Whether you are a salaried employee, a business owner, or a freelancer – choosing the correct ITR form is crucial.
Read our detailed guide and avoid penalties.
The time for Income Tax Return (ITR) filing has arrived, and most taxpayers ask one common question:
Which ITR form should I file?
Filing the wrong ITR form can result in your return being rejected, a notice being issued, and the need to refile your return.
That’s why selecting the correct form is essential.
Here, we present a simple guide for every ITR form applicable for AY 2025-26 (i.e., FY 2024- 25).
Why Are There Different ITR Forms?
The Income Tax Department has created different ITR forms for various categories of taxpayers – such as salaried individuals, business owners, professionals, companies, and trusts.
Each form is based on your income source, type of business, and annual income.
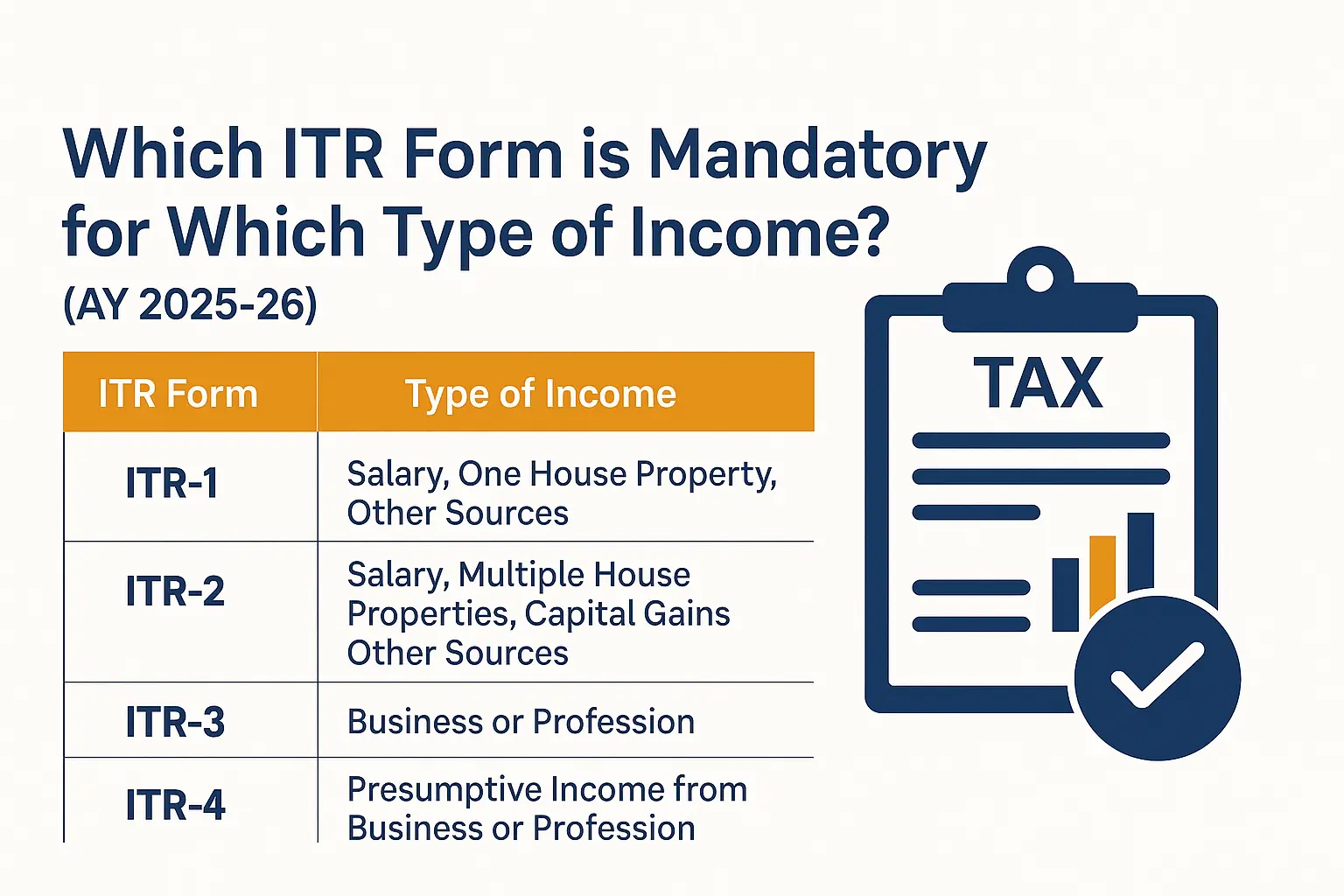
Complete List of ITR Forms (Who Should File Which Form)
1. ITR-1 (Sahaj)
- Who can file:
- Salaried individuals, pensioners, or those with income from one house property
- Total income up to ₹50 lakh
- Agricultural income up to ₹5,000
- Who cannot file:
- Individuals with capital gains, business income, or more than one property
- NRIs or those holding directorship/unlisted company shares
- Who can file:
2. ITR-2
- Who can file:
- Individuals with income from salary, pension, multiple house properties, capital gains, or other sources
- Both residents and NRIs
- Who cannot file:
- Those with business or professional income (they must use ITR-3)
3. ITR-3
- Who can file:
- Individuals/Hindu Undivided Families (HUF) with business or professional income
- Freelancers, doctors, lawyers, chartered accountants, consultants
- Partners in a partnership firm (but not the firm itself)
- Who cannot file:
- Individuals with no business/professional income (they should use ITR-1/2)
4. ITR-4 (Sugam)
- Who can file:
- Those opting for the presumptive taxation scheme (Sections 44AD, 44ADA, 44AE)
- Individuals, HUFs, and firms (excluding LLPs)
- Business turnover up to ₹2 crore or professional receipts up to ₹50 lakh
- Who cannot file:
- Non-residents or directors/shareholders in unlisted companies
5. ITR-5
- Who can file:
- Partnership firms, LLPs, AOP (Association of Persons), BOI (Body of Individuals), societies, and local authorities
- Who cannot file:
- Individuals and HUFs
6. ITR-6
- Who can file:
- All companies (except those claiming exemption under Section 11)
- Who cannot file:
- Companies registered under Section 11 (religious or charitable institutions)
7. ITR-7
- Who can file:
- Trusts, NGOs, political parties, research institutions, and charitable organizations
- Those filing returns under Sections 139(4A), 139(4B), 139(4C), 139(4D)
ITR Forms and Applicable Income Types (AY 2025-26)
| ITR Form | Who Can File | Applicable Income Sources |
|---|---|---|
| ITR-1 | Salaried, pensioners, one house, income up to ₹50 lakh | Salary, interest, small agriculture income |
| ITR-2 | Individuals, NRIs | Salary, multiple houses, capital gains, other income |
| ITR-3 | Business/professionals | Business, profession, salary, capital gains |
| ITR-4 | Presumptive income scheme taxpayers | Business/profession (within turnover limits) |
| ITR-5 | Firms, LLPs, AOP, BOI | Business/income |
| ITR-6 | Companies (except under Section 11) | All corporate income |
| ITR-7 | Trusts, NGOs, religious institutions | Charitable or specific income |
Common Mistakes Taxpayers Make
- Filing ITR-1 despite having both salary and capital
- Freelancers filing ITR-4 (when ITR-3 is correct).
- LLPs filing ITR-4 (they must use ITR-5).
Conclusion
Selecting the correct ITR form is the most important step in your tax filing process.
If you’re feeling confused about ITR Filing 2025, our team at JSTAX.in can help you with:
- Choosing the correct ITR form
- Document collection and filing
- Avoiding penalties and ensuring fast processing
Contact us today and make your tax filing stress-free!